In an era marked by rapid digital transformation, the significance of Operational Technology (OT) has reached new heights. OT encompasses the hardware and software designed for monitoring and controlling physical devices and processes within various industries such as manufacturing, utilities, and transportation. These systems are critical for the efficient functioning of essential sectors. However, as reliance on OT grows, so does the threat landscape associated with these systems. Cybersecurity risks to OT are escalating dramatically, threatening not only business operations but also public safety and national security.
The integration of cutting-edge technologies, including the Internet of Things (IoT), amplifies the exposure of OT frameworks to cyber threats. Hence, adopting a well-defined cybersecurity framework becomes imperative for organizations aiming to reinforce their defenses while remaining compliant with industry standards.
In this blog post, we will delve into how organizations can implement a structured Cybersecurity Framework to secure their OT systems effectively. We will also discuss the crucial role of compliance software in bolstering defenses against cyber threats.
Understanding OT Systems and Their Vulnerabilities
The Nature of OT Systems and Their Risks
Operational Technology includes various systems integral to critical industrial functions, such as Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems and Industrial Control Systems (ICS). These systems play a vital role in controlling machinery, monitoring production processes, and collecting real-time data across industries, including oil and gas, manufacturing, power generation, and water treatment.
Despite its indispensable role, OT is frequently exposed to significant vulnerabilities, including:
- Outdated Technology: Many OT environments still operate legacy systems that lack modern security features, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals. Neglected legacy systems are unlikely to receive regular updates, thus remaining vulnerable to known exploits.
- Inadequate Segmentation: Often, OT networks are not sufficiently segmented from IT systems, permitting attackers who breach the IT network to gain access to the less secure OT environments. This lack of segmentation drastically increases the potential for data breaches and operational disruptions.
- Limited Awareness: Employees may not receive sufficient training regarding cybersecurity best practices, leading to poor decision-making and susceptibility to phishing schemes or other negligent behaviors.
These vulnerabilities can lead to severe incidents, including data breaches, operational downtimes, and catastrophic impacts on critical infrastructure. A thorough understanding of these threats is essential for any organization aiming to mitigate risks effectively.
The Spectrum of Cyber Threats in Operational Technology
The array of cyber threats targeting OT is diverse and continually evolving. Ransomware attacks, Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, and targeted intrusions by nation-state actors exemplify the risks facing organizations. As cybercriminal strategies grow increasingly sophisticated, organizations must adapt their defensive measures accordingly to react to the transforming threat landscape.
The Importance of a Cybersecurity Framework in Protecting OT Systems
Using the Cybersecurity Framework to Strengthen OT Security
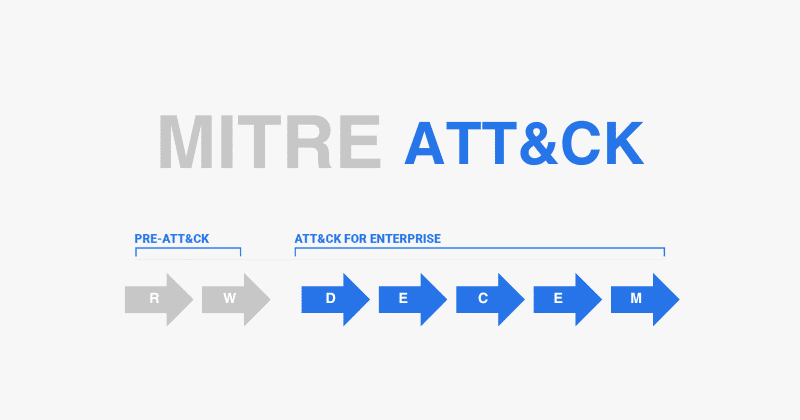
To effectively manage and mitigate risks within OT environments, a structured cybersecurity approach is vital. The Cybersecurity Framework established by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) offers a robust methodology that organizations can adapt to the distinct challenges posed by OT systems. This framework consists of five fundamental components: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover.
- Identify: Organizations should initiate the process by thoroughly assessing their hardware and software assets while understanding the associated cybersecurity risks. This phase involves conducting regular audits, inventory checks of OT systems, identifying critical assets, and performing risk assessments to establish a security baseline.
- Protect: Deploying appropriate safeguards to limit or contain the impacts of potential cybersecurity events is critical. Best practices may include installing firewalls, ensuring effective network segmentation, adopting the principle of least privilege, and implementing physical security measures.
- Detect: Continuous monitoring is indispensable for identifying anomalies and imminent threats within OT systems. Organizations can leverage Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems to enhance their detection capabilities.
- Respond: Organizations must have a well-defined incident response plan ready for deployment in the event of a cybersecurity incident. This plan should encompass predefined communication protocols and clearly assigned roles within the response team.
- Recover: Restoring systems and processes post-incident while using lessons learned to reinforce defenses is crucial for long-term cybersecurity resilience.
Implementing Best Practices for OT Cybersecurity
Actionable Best Practices for Enhancing OT Security
While a structured framework is essential, implementing effective security measures in OT environments necessitates a proactive mindset. Below are practical best practices that organizations can adopt to heighten their cybersecurity efforts:
- Regular Risk Assessments: Conducting frequent evaluations of OT systems helps identify vulnerabilities and assess the efficacy of existing controls.
- Software Updates: Keeping the software and firmware of OT devices current is paramount. Regular updates ensure that known vulnerabilities are patched.
- Employee Training: Continuous education on cybersecurity best practices promotes a culture of security awareness within the workforce.
- Incident Response Planning: Organizations should create a detailed incident response plan specifically tailored to their OT systems.
- Collaborating with Compliance Software Vendors: Engaging experienced compliance software providers can streamline adherence to industry regulations and standards.
- Continuous Improvement Mindset: Cybersecurity is an ongoing endeavor. Regularly reviewing and refining security strategies will ensure organizations can adapt to emerging threats effectively.
Conclusion
Securing Operational Technology systems against cybersecurity threats is of utmost importance. Utilizing a structured Cybersecurity Framework significantly enhances an organization’s defenses. By understanding the inherent vulnerabilities in OT and implementing best practices, businesses can lay down a solid foundation for their cybersecurity initiatives.
Ongoing vigilance, continuous assessments, and the integration of advanced compliance software into cybersecurity strategies will bolster an organization’s ability to fend off potential attacks. It is crucial for companies to actively implement measures to secure their OT environments, thereby protecting critical infrastructure and contributing to a more resilient future.
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the urgency of taking decisive action to safeguard operational technology systems becomes increasingly evident. Ensuring trust among stakeholders and customers hinges on prioritizing cybersecurity today, ultimately fostering a more secure and efficient operational ecosystem for tomorrow.